Transcription
factors (TFs), found in all living organisms, are proteins involved in the
control and regulation of gene expression. The function of these regulatory
proteins is to activate or inhibit transcription of DNA by binding to specific
DNA sequences. TFs are characterized by their DNA-binding domains (DBDs), among
them, the helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain is the most
prevalent in prokaryotic genomes.
The
large number of TF protein sequences available demands user-friendly databases
to facilitate inter-genomic and intra-genomic analyses. We have therefore
developed a novel resource, the P2TF (Predicted Prokaryotic Transcription
Factors) database, that contains the TFs of all
available bacterial and archaeal genomes, and 43 metagenomes. Our objective was to provide an easy to use
environment for validation by experts, according to their fields/organisms of
interest, with the data being completely available and consultable by all of
the scientific community.
From
the P2TF website the user can:
Browse
genome and metagenome TF predictions and manually
curated proteins
Search
for a sequence id or domain family
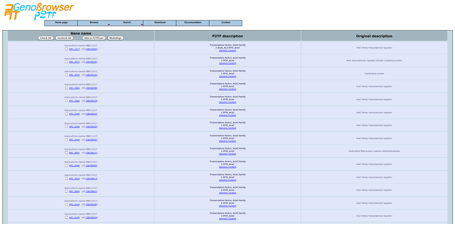
The
P2TF homepage contains a navigation bar that allows database browsing. Among
the menus, users will also find P2TF Browse, which links directly to sortable
lists of analysed genomes, plasmids and metagenomes.
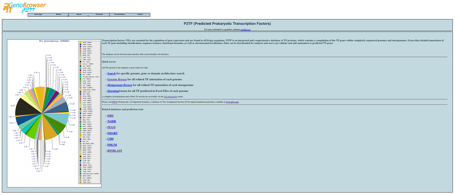
The
P2TF database contains the TFs of all available bacterial and archaeal genomes, and 43 metagenomes.
The
P2TF homepage contains a navigation bar that allows database browsing. Among
the menus, users will also find Browse,
which links directly to sortable lists of analysed genomes, plasmids and metagenomes.
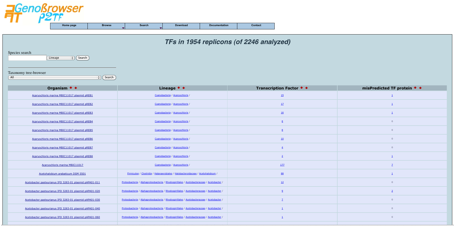
The
selection of a microbe or microbiome displays the
result of the P2TF analysis process.
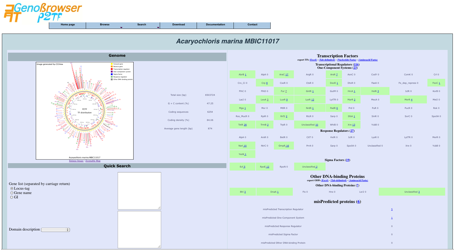
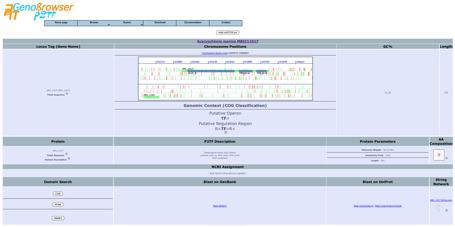
The
page shows global counts of the different categories of TFs and detailed class
counts of each category. Each class result provides a clickable link to a
detailed gene list.
It shows also a
search module, based on:
- locus-tag
- gene name
- gi number
- domain
Selecting
an object from the list identifiers displays a detailed gene description page
with an image representing the gene in the appropriate frame. Red vertical
lines represent stop codons and green lines represent potential start codons.
Blast searches
can be performed for the sequence, using external links to numerous databases.
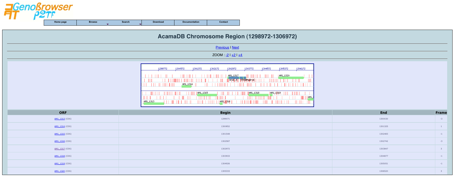
The gene
description page contains a link to a cartographic gene context (Chromosome
Region View), with several options such as zooming in or out, moving along the
chromosome, displaying genes in upstream or downstream regions and drawing
genes.
A second menu,
P2TF Search, provides several search modes that allows users to request genes
of all the database, on the basis of their locus-tag,
gene name, gi number or domain possession. A supplemental
search mode allows users to accede specifically to a genome of interest or a
group of genomes, using a taxonomy tree-browser.

The search module
builds search output as a gene list that is linked to a full description for
each selected gene (see above).
P2TF was designed
to allow download of TF data in tab-delimited format and generates a file
compatible with spreadsheet programs such as Excel. Users can also download for
each genome and metagenome a multi-Fasta file (nucleotide or protein sequences).

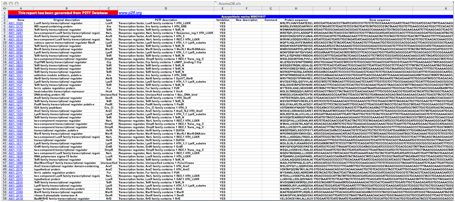
An example of an Excel file output.